Actinic Cheilitis
Definition
Actinic cheilitis is a chronic degenerative disorder of the lower lip (with sparing of the commissures). This is a type of actinic keratosis which classically occurs on the lower lip and is directly related to long-term sun exposure.
Ætiology
Long-term exposure to sunlight.
Clinical Features
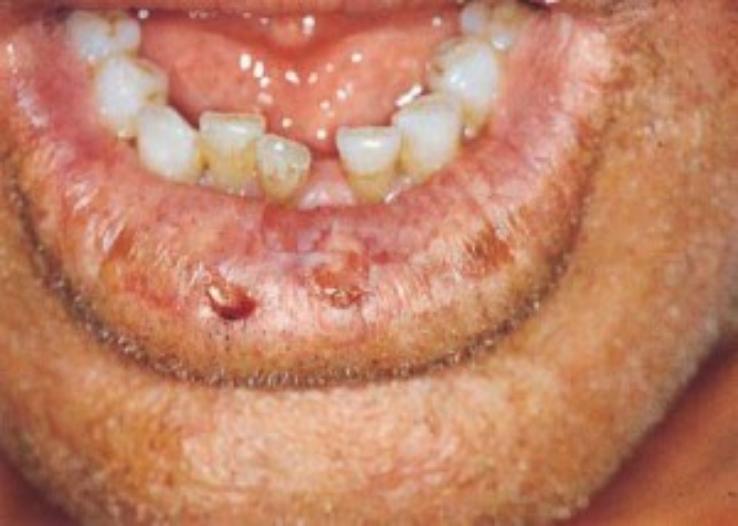
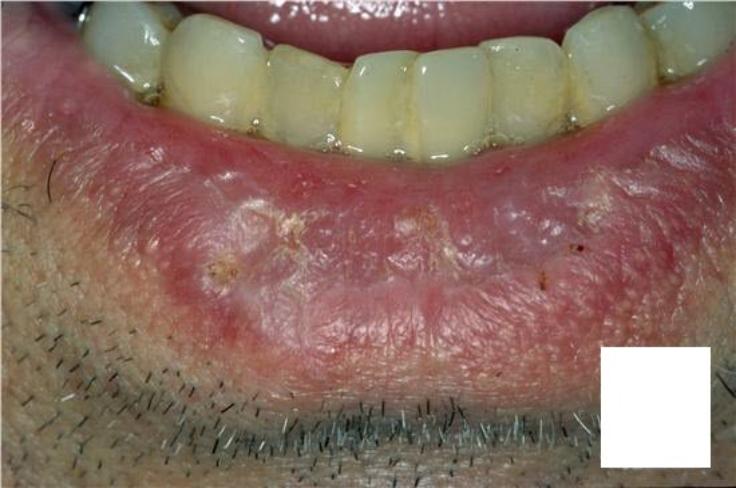
In the early stage, mild erythema (reddening) and œdema (swelling) followed by dryness and fine scaling of the lower lip vermilion border (the junction between the lip and skin) are the presenting signs.
As the lesion progresses, the epithelium (skin) becomes thin and smooth, with small whitish gray areas intermingled with red regions and scaly formations. Erosions (ulcers) and tiny nodules may develop.
The vermilion appears atrophic (thinned) and pale with a glossy surface and loss of demarcation at the vermilion border. With progression, fissuring and ulceration can occur along with crusting or scaling. Epithelial atrophy and elastosis are seen histologically and these changes are irreversible. Areas of persistent ulceration should be biopsied due to a 6 – 10% rate of malignant transformation.
The lesion is pre-malignant and usually occurs in fair-skinned men over 50 years of age, 4 – 8th decade of life and who have had outdoor jobs / activities.
Laboratory Tests
Histo-pathological examination.
Differential Diagnosis
The following conditions should be considered before making a diagnosis of actinic cheilitis:
- Leukoplakia
- Lichen Planus
- Lupus erythematosus
- early Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Cheilitis due to radiation.
Treatment
Protection of lips from sunlight. Vermilionectomy in severe cases. Treatment of malignancy is primarily surgical; however, a trial of topical chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil can be used with early lesions.
Prophylactic laser ablation or vermillionectomy may be performed in cases where malignant transformation has not yet occurred.
Close long-term follow-up is indicated, as these patients are at risk for additional cancers associated with solar damage.
Useful Articles & Websites
New Zealand Dermatological Society (DermNZ)
American Academy of Oral Medicine
J Canadian Dent Assn 2007. Clinical Practice. Exfoliative Cheilitis – Report of a Case
Eur J Dent 2011. Actinic Cheilitis. A Case Report & a Review of the Literature
World J Clin Cases 2014. Precancerous Lesions of Oral Mucosa
J Ind Acad Oral Med Radiol 2015. Actinic Cheilitis. A Review
British Association of Dermatologists 2016. Actinic Keratosis
Int J Health Sci & Res 2019. Actinic Cheilitis. A Case Report with Review of Literature
Maxillofac Plast & Recon Surg 2019. Proper Management of Suspicious Actinic Cheilitis