Novel Oral Anti-Coagulants (NOAC’s) & Oral Surgery
Dabigatran, Apixaban and Rivaroxaban are novel / new oral anti-coagulants (NOAC’s) that are alternatives to the coumarins (e.g. warfarin) in selected groups of patients for certain indications.
These medications are Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (Dabigatran) & Factor Xa Inhibitors (Rivaroxaban & Apixaban).
These drugs are orally administered, have predictable pharmacokinetics and dose response, do not require monitoring & have an acceptable safety profile when used appropriately, & so avoid many of the disadvantages & possible complications of warfarin and heparin.
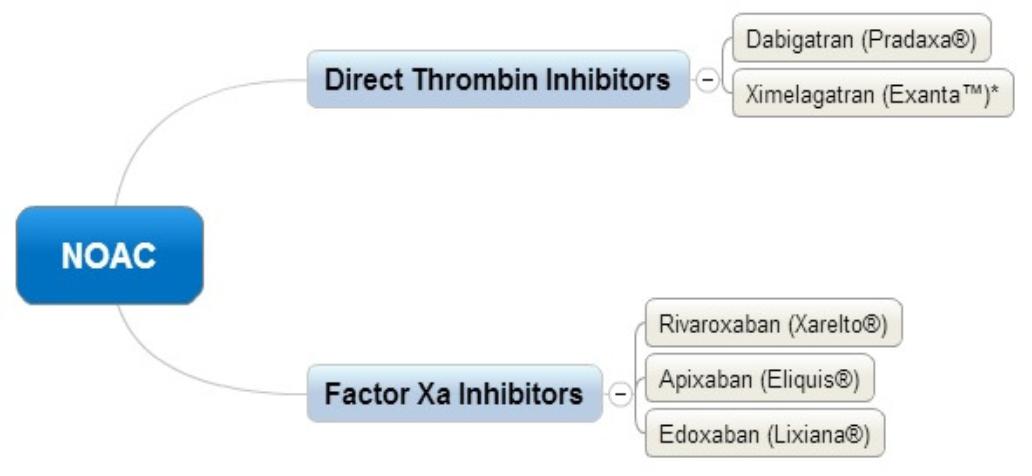 Novel Oral Anti-Coagulants (NOAC’s)Coagulation monitoring is usually not required for rivaroxaban or dabigatran and reliable tests are not available.
Novel Oral Anti-Coagulants (NOAC’s)Coagulation monitoring is usually not required for rivaroxaban or dabigatran and reliable tests are not available.
There are no evidence-based guidelines for the dental management of patients receiving these agents. However, because of their predictable & stable anticoagulant effects, comparable bleeding risks, & lower risk of drug interaction, dental management may be safer and easier with these drugs.
However, more scientific evidence, time, and experience is needed.
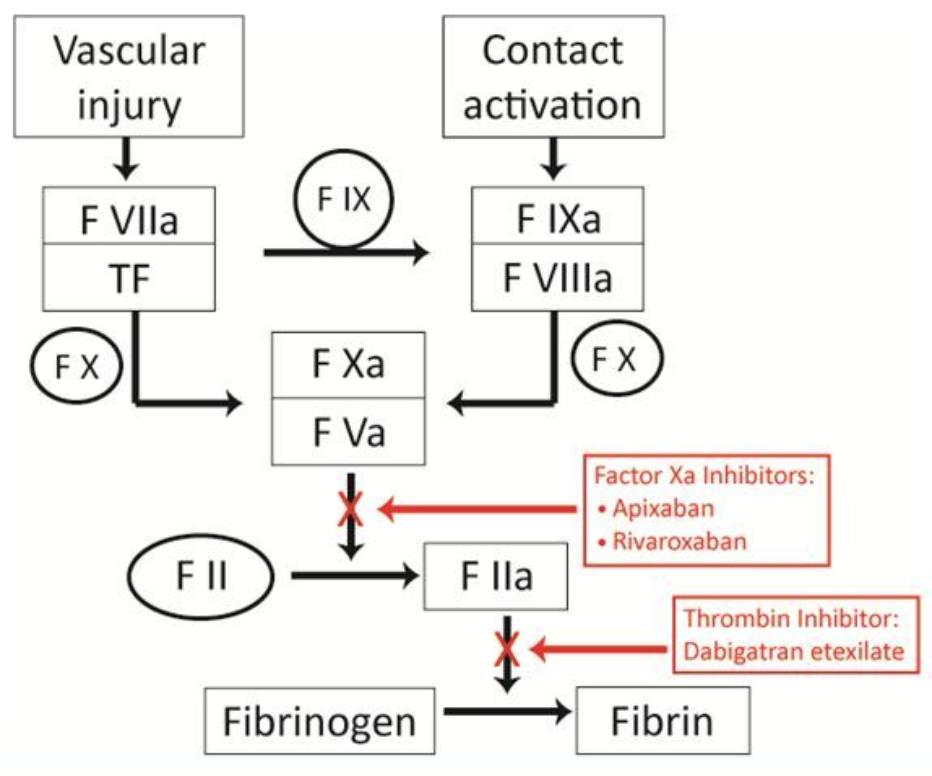 NOAC’s & the Clotting Pathway
NOAC’s & the Clotting Pathway
 Treatment Algorithm for Patients on NOAC’s
Treatment Algorithm for Patients on NOAC’s
Useful Articles & Websites
Scottish Dental Clinical Effectiveness Programme
Thromb Haemost 2010. Management of dental extraction in patients undergoing anticoagulant treatment.
BDJ 2013. Letters to the Editor. New Anticoagulants
BDJ 2013. The Changing Face of Oral Anticoagulants
BDJ 2013. Anticoagulant Update
J Clin Exp Dent 2013. Alternative to oral coumarin anticoagulants. Considerations in dental care.
Aust Dent J 2014. Protocol in Managing Oral Surgical Patients taking Dabigatran
BDJ 2014. Pharmacology. A New Bleeding Issue
BDJ 2014. Dabigatran (Pradaxa) – Surgeon’s Friend or Foe
J Irish Dent Assoc 2014. New Oral Anticoagulants & their Implications for Dental Patients
Post-Treatment Advice for Patients on Novel Oral Anti-Coagulants (NOACs).