Soft Tissue Damage
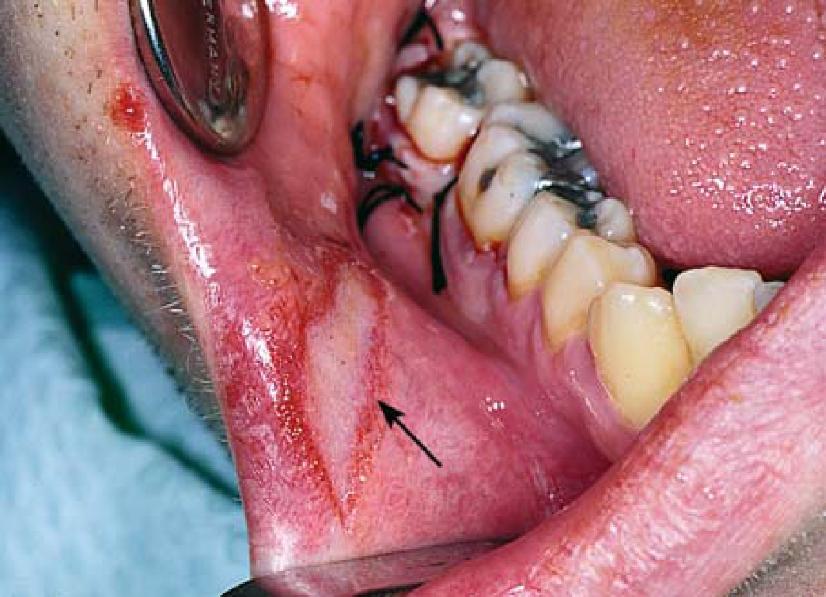
Careless tissue retraction with a tissue retractor (such as an Austins or Rake Retractor) can lead excoriation and swelling, mainly around the lips and especially at the commissure.
This is more likely to occur under general anæsthesia than local anæsthesia.
This commonly occurs when the lips and commissures are trapped between a (periosteal) elevator (used as a flap retractor) and the neck of the elevator being used to extract wisdom tooth (third molar), especially if the extraction is difficult (poor visibility and surgical access). It is all too easy to get carried away with the extraction and neglect the soft tissues.
Lacerations to the soft tissues can be caused by careless handling of scalpels, elevators, forceps scissors and sutures.
Vaseline or moisturising cream should be applied to the lips, pre-operatively and peri-operatively.
Thermal Trauma
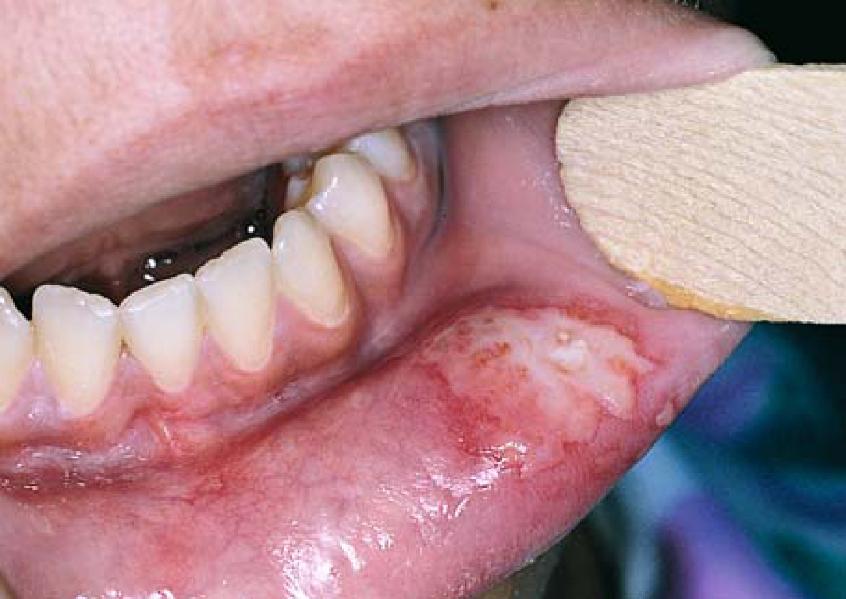
This happens with surgical drills that are not serviced regularly and properly maintained. These can be prone to bearing failure resulting in the drills overheating in normal use, especially if old burrs are used (in an attempt to save money and excess pressure is applied to the blunt bur because it cuts inefficiently). The hot drill then comes into contact all with the patients’ soft tissues resulting in a deep burn.
This is an indefensible disaster and the cosmetic results can be truly appalling.
If a surgical drill is ‘running hot’, it should be immediately discarded and sent for repair or condemned.
If a surgeon injures a patient with an instrument that is known to be defective, then they will only have themselves to blame when they are sued for negligence.
Poor vigilance while using an electrical cautery (diathermy) or laser is another indefensible cause of damage to surrounding soft tissues.
When these instruments are in use, non-conducting and non-reflective retractors should be used and in the case of lasers all surrounding areas should be protected by wet swabs. Extreme care should be used when using monopolar cautery to coagulate a blood vessel via a non-insulated pair of tissue forceps in case they should come into contact with the surrounding soft tissues.